
Our Products
Our wide Range of Products, designed to help your institute/Organization/Business grow exponentially
Home / What is OMR Sheets and How They Work
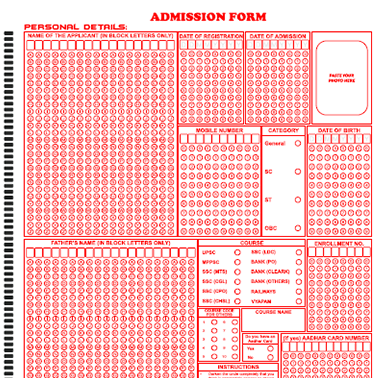
An OMR (Optical Mark Reader) sheet is a special type of paper used for capturing data, especially in exams and surveys. It has bubbles that candidates fill in and timing tracks that help machines read the sheet accurately.
OMR sheets usually collect personal and exam-related information, such as:
Candidate's Name
Date of Birth
Father's Name
Roll Number
Category
Address
Mobile Number
Date of Exam
Barcode/QR Code
Answers to exam questions
Advances in OMR Technology: New OMR technology now allows candidates to simply tick the bubbles instead of filling them completely. The software can recognize these tick marks, making it easier and faster for candidates.
OMR sheets are widely used in conditions where large amounts of data need to be collected quickly and accurately. Common use case are-
From school tests to professional entrance exams, especially those with multiple-choice questions.
Used in scientific, marketing, and statistical surveys to gather data.
Helps collect detailed personal information during registration processes.
Used in competitions like Olympiads and various entrance exams.
Used in hiring processes, especially for competitive exams.
Captures responses in educational and workplace settings.
Recently, OMR sheets have been used effectively for voting and tracking attendance.
Designing an OMR (Optical Mark Reader) sheet requires careful planning to make sure it works properly. Here’s how you can design an effective OMR sheet:
Optical Mark Recognition (OMR) is a method used to read marks made on specially designed sheets, like those used in exams and surveys. There are two main ways to process OMR sheets:
This is the traditional way of reading OMR sheets using a special machine.
First, a blank OMR sheet is scanned to create a reference template.
The machine identifies important parts like:
The machine then sets up fields based on this template.
Once the template is ready, all filled OMR sheets are scanned.
The machine reads the marked bubbles based on the template.
This newer method uses software to read and process OMR sheets, making the process easier and more flexible.
This method uses advanced software that can read simple tick marks instead of filled bubbles.(You can try Yomark OMR Software)
User-Friendly: Easier for candidates to just tick the circles.
Flexible: The software can adapt to different sheet designs easily.
Cost-Effective: You can use regular scanners instead of expensive machines.
Reliable: Reduces the chances of mistakes, so results are more dependable.
Depends on Software Quality: The accuracy depends on how good the software is.
Initial Setup: It may take some time to set up and test the system.
Both OMR methods are used to read and process marked data from sheets.
OMR Machine Methodology is best for traditional setups with standard formats.
OMR Software Methodology is a modern, flexible, and cost-effective solution, especially useful if you need more adaptability.
Description: A widely used security feature that helps manage duplication and identify sheets after scanning.
Details: The barcode is a series of lines containing embedded codes. Various types of barcodes are available, chosen based on the size and space on the OMR sheet.
Description: A modern security feature, QR codes are small boxes containing a unique code or number.
Details: QR codes are used to prevent duplication and identify sheets upon scanning. They are scanned using a QR code reader.
Description: A highly secure feature, holograms are colorful, metallic stickers applied to OMR sheets.
Details: Holograms are difficult to duplicate and help prevent fraud. Their distinctive appearance makes them a reliable security measure.
Description: Litho codes are alphanumeric combinations printed on OMR sheets.
Details: These codes are used to control duplication and identify sheets after scanning, providing an extra layer of security.
Description: Sequential numbering is used to track OMR sheets and minimize duplication.
Details: Each sheet is assigned a unique number, which helps in verification and tracking. The number is captured in images for identification purposes.
Description: UV printing involves using ink that is only visible under UV light.
Details: Certain logos and characters are printed with UV ink, which is invisible to the naked eye but visible under UV lamps. This ensures high-level protection against duplication.
Description: Anti-copy ink is used to prevent unauthorized copies of OMR sheets.
Details: When photocopied, the anti-copy ink reveals a COPY watermark, making it clear that the document is not an original. This feature helps in preventing duplicate copies.
By incorporating these security features, OMR sheets can be better protected against duplication and tampering, ensuring the integrity of the data collected.
OMR (Optical Mark Reader) sheets are versatile tools used in various fields for efficient data collection and processing. Here’s how they are applied in different areas:
Purpose: Used for registering candidates.
Size: Legal (8.25 x 14).
Information Included: Personal details such as Name, Father's Name, Date of Birth, Address, Category, Qualification, Email, Mobile Number, and postal details.
Process: Candidates fill in the bubbles on the form. The sheet is scanned, and an admit card with Roll Number and center details is generated.
Advantages:
Fast processing and result preparation
100% accuracy
Efficient and error-free
Reduced chances of manipulation
Cost-effective
Purpose: To test students’ mental aptitude in subjects like Science, Math, and Reasoning.
Advantages:
Quick processing and result generation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Low manipulation risk
Cost-effective
Purpose: For entry into professional institutes and courses (e.g., IIT, JEE, MBA, MBBS).
Advantages:
Rapid processing and result preparation
100% accuracy
Efficient and error-free
Reduced chances of manipulation
Cost-effective
Purpose: For recruitment and professional exams.
Advantages:
Fast processing and result preparation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Low manipulation risk
Cost-effective
Purpose: To identify talented students at various levels (e.g., district, state, national).
Advantages:
Quick processing and result generation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Low manipulation risk
Cost-effective
Purpose: Used by government departments, public sector, and private companies for hiring.
Advantages:
Fast processing and result preparation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Low manipulation risk
Cost-effective
Purpose: For reliable and large-scale data collection.
Advantages:
Quick processing and result generation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Reduced chances of manipulation
Cost-effective
Purpose: Used by marketing companies for quick and accurate survey results.
Advantages:
Fast processing and result preparation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Low manipulation risk
Cost-effective
Purpose: Ideal for handling large volumes of data.
Advantages:
Quick processing and result preparation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Reduced manipulation risk
Cost-effective
Purpose: For accurate and reliable inventory tracking.
Advantages:
Fast processing and result generation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Reduced chances of manipulation
Cost-effective
Purpose: For collecting feedback efficiently.
Advantages:
Fast processing and result preparation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Low manipulation risk
Cost-effective
Purpose: For handling ballot forms in elections.
Advantages:
Quick processing and result generation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Reduced manipulation risk
Cost-effective
Purpose: For tracking attendance in educational and corporate settings.
Advantages:
Fast processing and result preparation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Low manipulation risk
Cost-effective
Purpose: For evaluating employee performance and promotions.
Advantages:
Fast processing and result preparation
Accurate and efficient
No human error
Reduced chances of manipulation
Cost-effective